How price controls reallocate surplus.
A nonbinding price floor leads to a n.
Quantity of zero units.
D binding price ceiling.
Has an effect only when it is set above the market price.
Price and quantity controls.
D quantity of zero units.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
Note that the price floor is below the equilibrium price so that anything price above the floor is feasible.
Unfortunately it like any price floor creates a surplus.
Legislating a minimum wage is commonly seen as an effective way of giving raises to low wage workers.
A binding price floor.
Another way to think about this is to start at a price of 100 and go down until you the price floor price or the equilibrium price.
C nonbinding price floor.
3 suppose the government of the oil rich country saudi arabia sets gasoline prices at 0 25 per gallon when the market price is 1 50.
Taxation and dead weight loss.
A non binding price floor is set below the equilibrium price.
B remain the same.
You might also like.
In this case it is a surplus of.
Has little effect on market activity.
If a government price floor of 1 10 is imposed on this market an inefficiency will result in the form of a of million pounds of butter.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
In the case of a binding price floor economists expect the quality level of a good to.
Think of the airline example from class a rise.
A price floor is a form of price control another form of price control is a price ceiling.
B nonbinding price ceiling.
Nothing is preventing prices from rising so nothing will change.
The latter example would be a binding price floor while the former would not be binding.
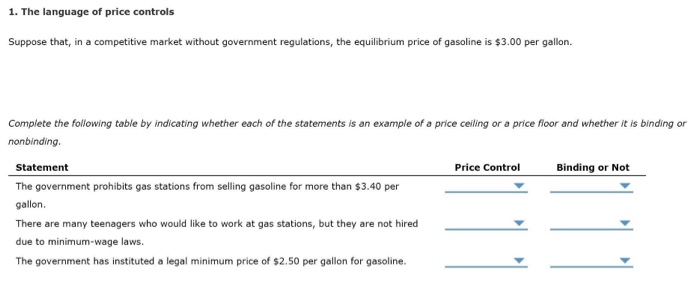
Price ceilings and price floors.
A good example of how price floors can harm the very people who are supposed to be helped by undermining economic cooperation is the minimum wage.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
This is a price floor that is less than the current market price.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
There are two types of price floors.
A price floor or minimum price is a lower limit placed by a government or regulatory authority on the price per unit of a commodity.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
Minimum wage and price floors.
A price ceiling a.
A nonbinding price ceiling leads to a n a.
If quantity supplied equals 80 units and quantity demanded equals 85 units under a price control then it is a.
This changes nothing because at this price there is a shortage which drives prices up.